WHY IS PREVENTION IMPORTANT?
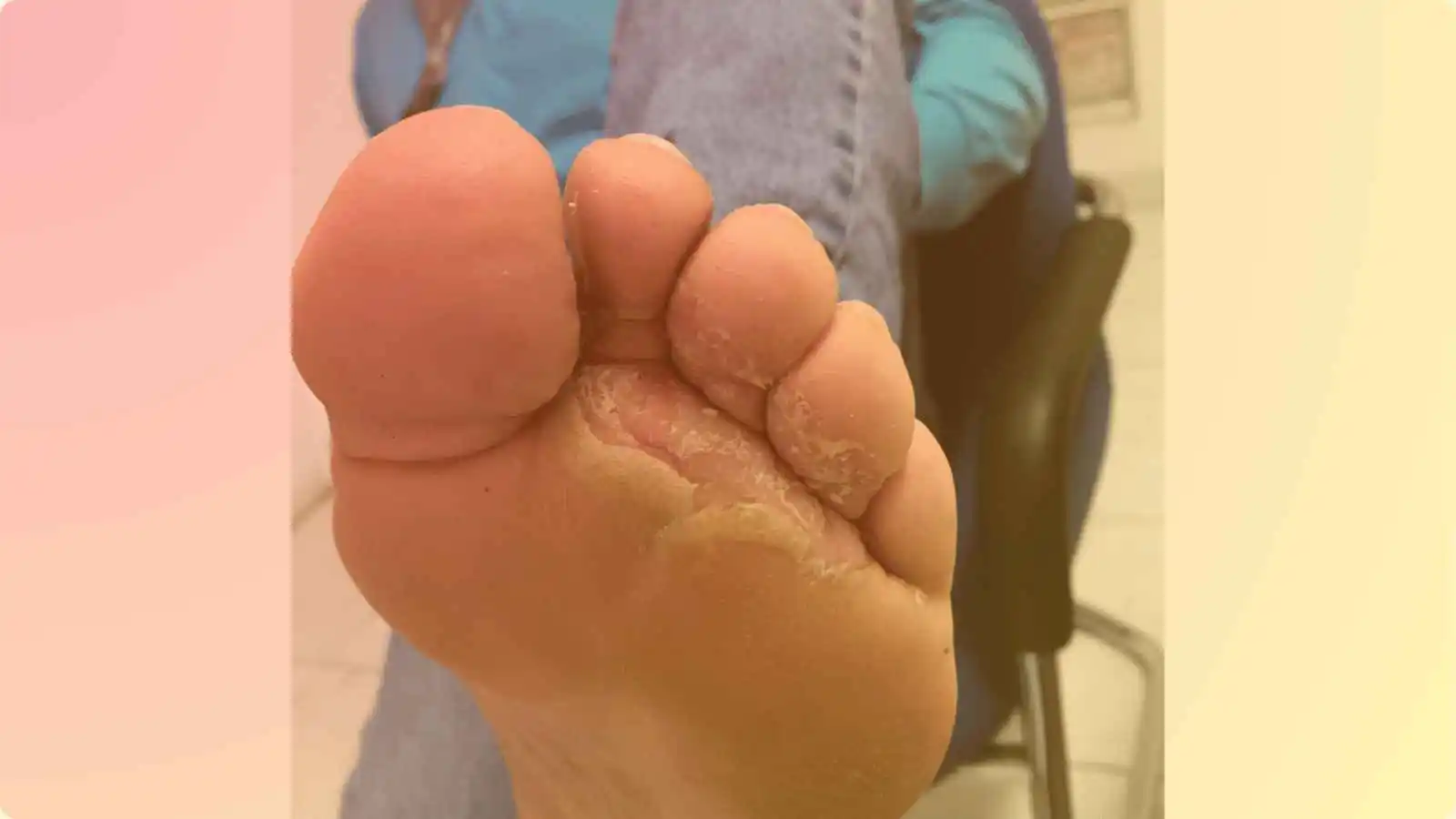
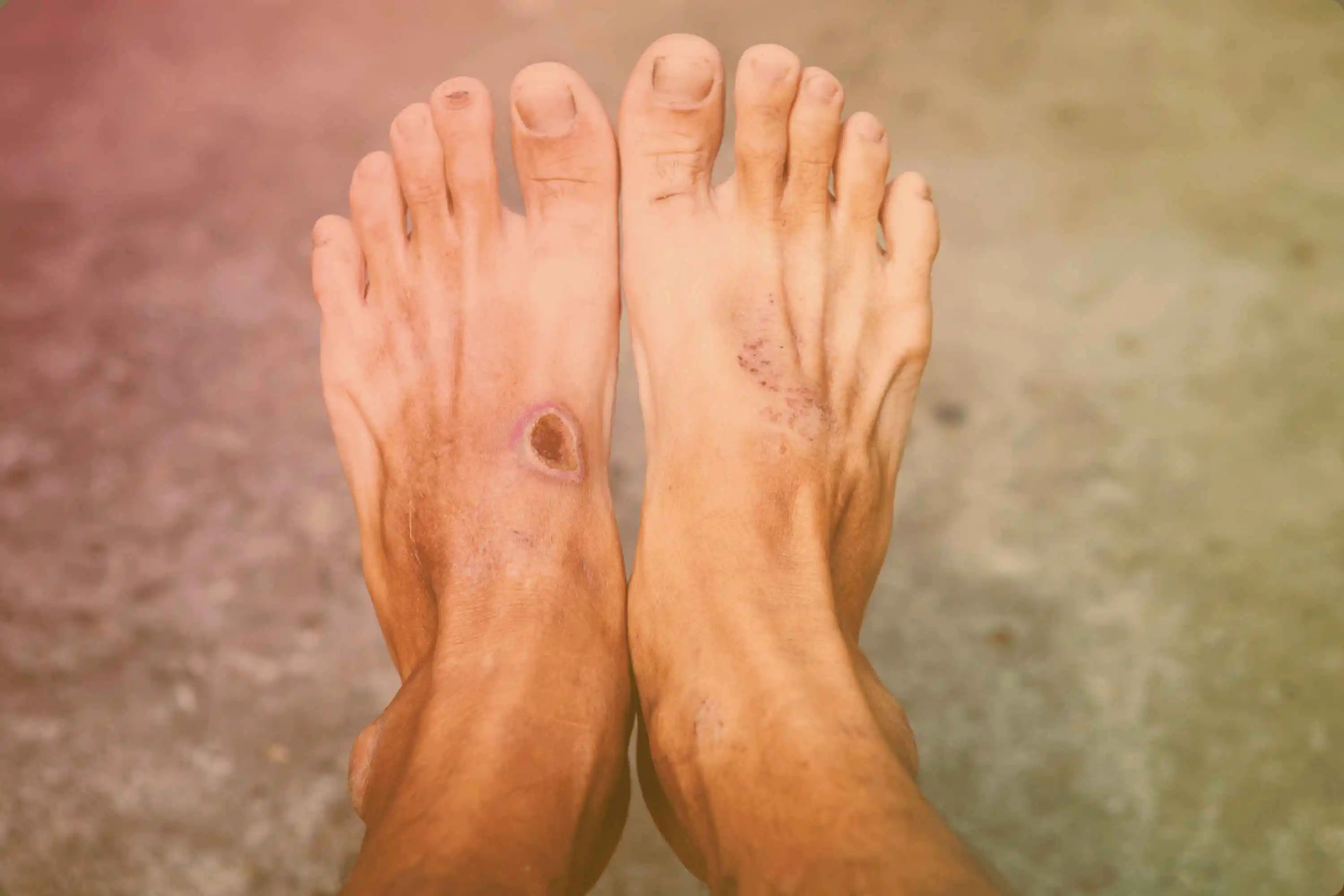
Diabetic foot is a complication majorly seen in diabetic patients. Diabetic foot is defined as, there are ulceration of the lower limb associated with peripheral neuropathy In this, there is loss of sensation & reduced blood flow causes ulceration. In that tissues death occurs & then less oxygen & blood supply cause gangrene. It is called as diabetic gangrene. Diabetic gangrene is a life threatening disease.
Complications of Diabetic foot:
- Cellulitis
- Osteomyelitis
- Sepsis
Key Homeopathic Medicines for Diabetic Foot
Certain homeopathic medicines have been traditionally used to manage complications of diabetes, including diabetic foot. Selection of medicines should always be guided by a qualified homeopathic practitioner.
Acid Phos
Suited for cases where diabetes occurs due to nervous exhaustion. Signs may include frequent urination, weakness, emaciation, and mental fatigue.
Syzygium Jambolanum
Known for reducing blood and urine sugar levels. Particularly useful for chronic ulcers in diabetic patients. May help with healing of diabetic foot ulcers.
Uranium Nitricum
Used for excessive urine with high sugar content, great thirst, and general debility. May help reduce urine quantity and support metabolic balance.
Kali Phos
Indicated for those experiencing anxiety, nervous exhaustion, and glandular decay. Can be supportive in cases with gangrenous tendency and yellow urine.
Note: These medicines should only be taken under the supervision of a qualified homeopathic doctor. Individual treatment may vary based on the patient’s unique symptoms and constitution.
What are examples and symptoms of foot problems caused by diabetes?
In the most severe case, as mentioned above, due to a combination of decreased sensation and reduced blood flow to the feet, ulcers may develop. If the tissues continue to receive insufficient oxygen, tissue death (gangrene) occurs. Gangrene is a serious and potentially life-threatening condition. Other potentially serious problems that may develop include cellulitis (infection of the tissues beneath the skin) and osteomyelitis (infection of the bone); sepsis (the infection spreads to the bloodstream) also is possible.
People with diabetes are at increased risk for milder problems with the feet that are not specific to diabetes but may occur more frequently due to problems with the nerves and circulation to the feet.
Some of these conditions are:
- Calluses and corns, that may develop due to abnormal alignment of the feet or abnormal gait
- Fungal infections of the nails, which can appear as thickened, discolored, and at times brittle nails
- Tinea pedis, or athlete’s foot, a fungal infection of the skin of the feet
- Hammertoes, or bent toes due to muscle weakness.
- Bunions, or the angling of the big toe toward the second toe. The area of the bunion may become reddened and irritated, leading to callus formation.
- Ingrown toenails plz dont change the content i want line to line